In today’s digital-first world, combating fraud has become more essential than ever. Facial recognition software has emerged as a game-changing technology, transforming how organizations prevent and detect fraudulent activities. As fraudsters develop increasingly sophisticated methods to bypass traditional security measures, the need for innovative and reliable solutions has grown exponentially.
Facial recognition technology addresses this challenge by delivering highly accurate identification capabilities, strengthening security protocols across multiple industries. This article explores the critical role of facial recognition in modern fraud prevention, highlighting its seamless integration into identity verification and authentication processes and its effectiveness in staying ahead of an ever-evolving threat landscape.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is facial recognition software?
Facial recognition software is a state-of-the-art technology capable of identifying and verifying individuals by analyzing their unique facial characteristics. Using advanced facial recognition algorithms, the software maps key features such as the distance between the eyes, cheekbone structure, and lip contours to create a distinctive faceprint. This biometric security measure enables real-time recognition and authentication by matching the faceprint against a database of known profiles.
Unlike traditional security methods like passwords or PINs, face recognition provides a seamless and non-invasive way to verify a person’s identity. The technology captures an image, converts it into data, and cross-references it with stored records to confirm identity.
Banks, retailers, and airport security increasingly integrate facial recognition to prevent identity fraud. Additionally, law enforcement investigations leverage this technology to identify specific individuals from surveillance footage or social media images, aiding in criminal identification. As cyber threats evolve, facial recognition offers a proactive approach to protecting personal data, mitigating unauthorized access, and streamlining identity verification.
How does facial recognition work?
Facial recognition technology operates through an advanced process that combines machine learning and facial recognition algorithms to accurately verify and identify people. The process consists of three key steps: detection, analysis, and matching.
Detection
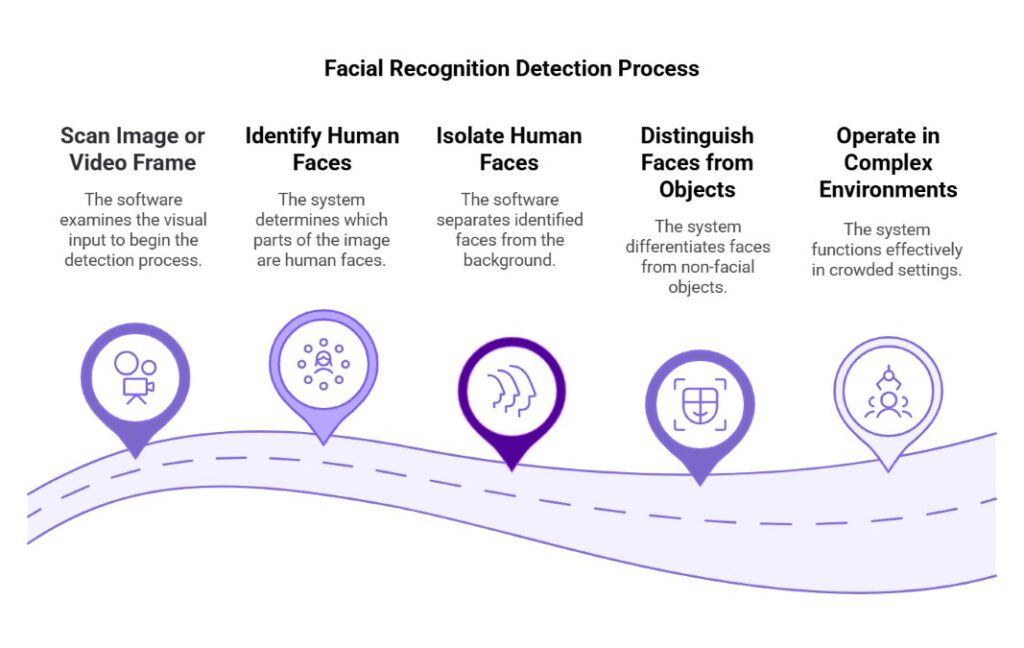
The software first identifies and isolates faces within an image or video frame. Using sophisticated computer vision techniques, it distinguishes human faces from other objects, even in complex or crowded environments.
Analysis
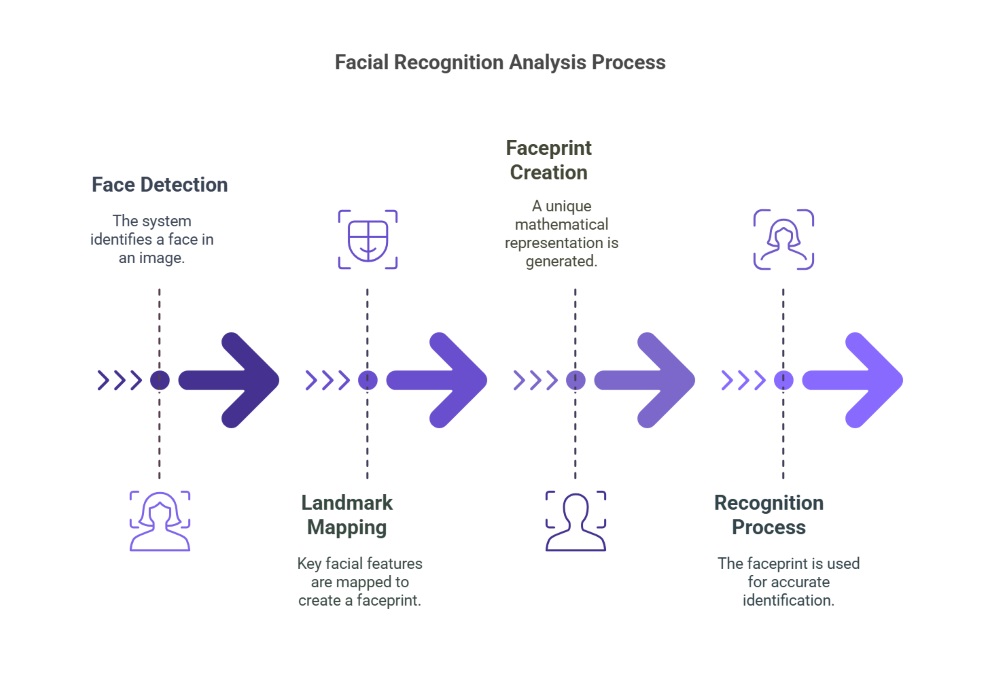
Once a face is detected, the system maps key landmarks, such as the eyes, nose, and mouth, to create a faceprint, a unique mathematical representation of facial features. This allows for accurate differentiation between individuals, even when expressions change or accessories like glasses or facial hair are present.
Matching
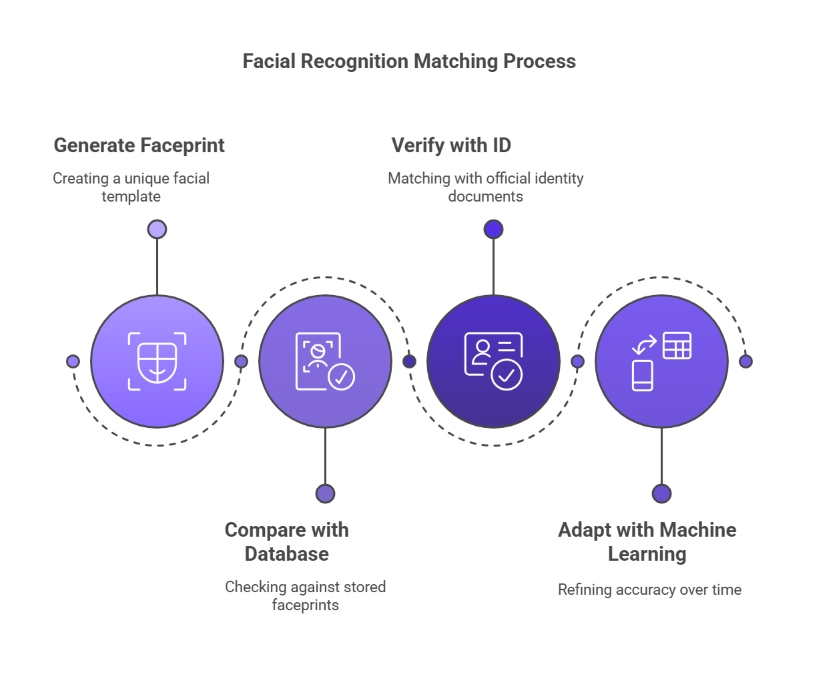
In the final step, the system compares the generated faceprint against a reference source. This could be a database of stored faceprints for authentication or an official identity document, such as a passport, for first-time verification. Machine learning continuously refines accuracy by adapting to subtle changes in facial appearance over time.
Facial recognition technology plays a vital role in real-time applications, such as unlocking smartphones and securing access to sensitive locations. It also supports forensic investigations by helping law enforcement verify identities from archived footage. Its ability to function effectively in varied conditions, including low-light environments and crowded spaces, highlights its reliability. By integrating with identity verification systems, facial recognition enhances security, reduces fraud, and ensures seamless, secure authentication.
Applications of facial recognition software
Facial recognition software is quickly becoming a cornerstone technology across various industries, transforming how organizations enhance security, verify identities, and deliver personalized customer experiences. Its capabilities go beyond basic identification, offering versatile solutions tailored to the unique needs of different sectors.
Financial services: Banks and financial institutions are increasingly leveraging facial recognition to bolster security. By incorporating this technology into authentication systems, they can safeguard sensitive information, prevent fraud in online banking, and provide seamless identity verification. Customers benefit from quick, secure transactions through facial scans, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access.
Retail: The retail industry is utilizing facial recognition to create more personalized shopping experiences, improve loss prevention and prevent retail fraud. Retailers can identify VIP customers, enabling staff to offer tailored services and promotions. At the same time, facial recognition systems enhance security by detecting known shoplifters and flagging their presence, thereby reinforcing theft prevention strategies.
Law enforcement and public safety: Facial recognition plays a key role in identifying suspects and locating missing persons. Authorities can match images captured in public spaces with databases of known individuals, improving their ability to track and apprehend suspects efficiently while maintaining public safety.
Healthcare: In healthcare, facial recognition helps streamline patient identification and protect sensitive medical information. Hospitals and clinics use facial scans to verify patient identities, minimizing administrative errors and improving check-in processes, ultimately enhancing overall patient care.
Airports and transportation: Facial recognition has become an essential tool in passenger processing. Airports use it to expedite check-ins and boarding by matching travelers’ identities with passport databases. This not only strengthens security but also reduces wait times, creating a more efficient and stress-free travel experience.
Education: Educational institutions are exploring facial recognition to simplify attendance management and strengthen campus security. Automated roll-call systems save time, while facial scans help monitor and control access to facilities, fostering a safer learning environment.
Facial recognition software’s applications continue to expand, offering innovative solutions that enhance security, streamline operations, and improve user experiences. As the technology evolves, it promises to unlock new possibilities across industries, from combating fraud to increasing operational efficiency.
Facial recognition software in fraud prevention
As fraud tactics become more sophisticated, facial recognition software has emerged as a powerful tool for enhancing security. By utilizing biometric data, this technology helps organizations prevent identity fraud and unauthorized access. Here’s how facial recognition is transforming fraud prevention strategies:
Strengthening identity verification
Facial recognition software enhances identity verification by comparing a live facial scan to an official ID rather than relying solely on pre-existing databases. During onboarding, the system captures a real-time image, matches it against the document’s photo, and verifies authenticity using advanced fraud detection techniques. This method provides a more secure and seamless alternative to traditional verification methods, reducing the risk of identity fraud while improving user experience.
Securing online transactions:
With the rise of e-commerce, securing online transactions has never been more critical. Facial recognition technology seamlessly integrates into payment systems and verifies users during purchases, ensuring the legitimate account holder initiates the transaction. This approach not only mitigates the risk of fraudulent transactions but also offers a user-friendly alternative to traditional multi-factor authentication methods.
Access control and monitoring:
For environments that require strict access to sensitive information or areas, facial recognition is a key tool. By granting or denying access based on real-time facial scans, organizations can protect confidential data and secure physical locations. Additionally, the system can maintain detailed logs of entries and exits, providing an auditable trail to strengthen compliance and security.
Detecting insider threats:
Insider threats pose a significant challenge for organizations, and facial recognition technology helps mitigate these risks. By monitoring employee movements and restricting access to specific areas, the software ensures only authorized personnel have access to critical locations. This proactive surveillance fosters trust while protecting essential assets from potential internal fraud.
Real-time surveillance and detection:
In sectors such as retail and finance, facial recognition plays a pivotal role in real-time surveillance. Systems continuously scan and compare faces against watchlists, enabling the swift identification of known fraudsters or suspicious individuals. This real-time capability empowers security teams to respond quickly and prevent fraudulent activities before they escalate.
By incorporating facial recognition technology into fraud prevention strategies, organizations can enhance security while streamlining operations. As advancements in this technology continue, its applications in fraud prevention are becoming increasingly sophisticated, offering a proactive and reliable defense against evolving threats.
How accurate is facial recognition?
Facial recognition technology has made remarkable strides in recent years, thanks to advancements in machine learning and algorithmic precision. However, its accuracy depends on several factors, including image quality, environmental conditions, and the diversity of training datasets.
High accuracy in controlled conditions: Under optimal conditions, such as clear images, stable lighting, and consistent angles, facial recognition software can achieve accuracy rates exceeding 99%. This reliability makes it particularly effective for applications like smartphone unlocking, where conditions remain relatively stable.
Challenges in real-world environments: In less controlled settings, external factors such as poor lighting, facial obstructions (e.g., hats or masks), and variations in expressions or angles can affect accuracy. Surveillance footage and crowded public spaces present additional challenges, often reducing the system’s ability to consistently identify individuals with the same level of precision.
Algorithmic advancements and bias reduction: Continuous improvements in machine learning help facial recognition systems adapt and refine their accuracy over time. However, algorithmic bias remains a critical issue. Historically, underrepresentation of certain demographics in training datasets has led to disparities in recognition rates across racial and gender groups. To address this, developers are prioritizing diverse data training and fine-tuning algorithms to ensure more equitable performance across all users.
Ethical considerations and regulatory standards: Despite its technological progress, facial recognition raises ethical concerns, particularly around privacy and surveillance. Organizations must implement these systems transparently and responsibly, ensuring they comply with evolving regulations. Many industries and regulatory bodies are now establishing guidelines to promote both accuracy and ethical deployment, including rigorous testing across diverse populations.
By understanding these factors, businesses and institutions can leverage facial recognition technology effectively while maintaining accountability. As research and innovation continue, ongoing improvements will help refine accuracy, enhance security, and expand the technology’s role in identity verification and fraud prevention.
Is facial recognition safe?
The safety of facial recognition technology depends on both its technical security and ethical implementation. As its adoption grows across industries, ensuring its responsible use requires strong data protection, privacy safeguards, and regulatory compliance.
Facial recognition systems process and store sensitive biometric data, making secure handling essential. Organizations must implement robust encryption techniques and strict storage protocols to prevent data breaches and unauthorized access. Strengthening cybersecurity measures reduces the risk of data exposure and enhances system integrity. At the same time, facial recognition’s ability to identify individuals in both public and private settings raises significant privacy concerns.
Without proper safeguards, the technology can enable intrusive surveillance and erode personal privacy. To mitigate these risks, organizations must establish clear policies on data collection, consent, and retention. Being transparent about how and why facial data is used keeps users informed and in control of their information.
Regulatory frameworks play a crucial role in guiding the ethical use of facial recognition. Compliance with international laws, such as the European Union’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), ensures organizations handle biometric data responsibly. These regulations set strict standards for user consent, data processing, and rights protection, aligning facial recognition practices with legal and ethical norms.
Despite advancements, facial recognition can exhibit biases that lead to accuracy disparities among different demographic groups. Addressing this issue requires rigorous testing, algorithm refinement, and diverse training datasets. Improving fairness in facial recognition strengthens reliability and prevents unintended discrimination.
Beyond technical and legal considerations, organizations must implement ethical oversight to ensure responsible deployment of facial recognition. Organizations must establish independent audits and advisory boards to evaluate the societal impact of the technology, detect potential biases, and maintain transparency. Regular assessments help align its use with ethical principles and public interest.
While facial recognition enhances security and operational efficiency, its safety ultimately depends on responsible implementation. Prioritizing data protection, privacy rights, and ethical guidelines allows organizations to deploy the technology securely while fostering public trust. As the field continues to evolve, ongoing engagement with regulatory and ethical developments will be critical for ensuring its safe and equitable use.
What is a confidence score in facial recognition software?
In facial recognition technology, a confidence score measures the system’s certainty when matching a scanned face to either a stored profile or an identity document. This numerical value, typically expressed as a percentage, indicates how closely the captured facial features align with the reference image.
How confidence scores work
When a facial recognition system analyzes an image, it generates a faceprint and compares it against a reference source. For identity verification, the system matches the faceprint to the photo on a submitted identity document, such as a passport or driver’s license. In authentication scenarios, it compares the faceprint to stored profiles in a database.
The confidence score reflects the degree of similarity, considering factors like facial landmarks, contours, and unique characteristics. A higher score suggests a stronger match, increasing the likelihood that the scanned face belongs to the correct individual.
Setting match thresholds
Confidence scores define acceptable match thresholds, influencing security protocols for identity verification and access control. Organizations adjust these thresholds based on their tolerance for false positives or negatives. High-security environments, for example, often require higher confidence scores to minimize the risk of unauthorized access and ensure greater system accuracy.
Balancing security and user experience
By leveraging confidence scores, organizations can fine-tune facial recognition systems to optimize both security and user convenience. This ensures precise identity verification while adapting the technology for various applications, from securing financial transactions to managing access in sensitive locations.
As facial recognition technology advances, refining confidence scores will remain essential for improving accuracy, mitigating bias, and strengthening fraud prevention across industries.
How Udentify can enhance facial rercognition security
Udentify provides a seamless and secure solution for identity verification, leveraging advanced technology to ensure accurate and reliable authentication. By integrating sophisticated recognition capabilities, it helps businesses prevent fraud, streamline access control, and enhance user experience.
Designed for industries where secure identity verification and authentication is essential, Udentify offers a balance of precision, efficiency, and compliance with data protection standards. Its intuitive approach ensures both security and convenience without compromising privacy.
To learn more about how Udentify can strengthen your verification processes, visit Udentify.
Facial recognition software FAQ
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
| What is facial recognition software? | Facial recognition software uses advanced algorithms to identify and verify individuals by analyzing facial features. It creates a unique faceprint and matches it against a reference image or database for authentication and security purposes. |
| How does facial recognition work? | The process involves three steps: detection (locating a face in an image or video), analysis (mapping key facial features), and matching (comparing the faceprint against a stored profile or identity document). |
| Where is facial recognition used? | Industries such as banking, retail, healthcare, law enforcement, and transportation use facial recognition for identity verification, fraud prevention, and access control. |
| How does facial recognition prevent fraud? | It strengthens identity verification by ensuring a live facial scan matches an official ID or stored faceprint. It also detects suspicious activity in real time, preventing unauthorized access and fraudulent transactions. |
| How accurate is facial recognition? | Under optimal conditions, accuracy can exceed 99%. However, factors like lighting, facial obstructions, and algorithmic bias can affect performance. Ongoing advancements help improve reliability across diverse demographics. |
| Is facial recognition safe? | When implemented responsibly, facial recognition enhances security while protecting personal data. Organizations must follow privacy regulations, use encryption, and establish ethical oversight to prevent misuse. |
| What is a confidence score in facial recognition? | A confidence score indicates how closely a scanned face matches a reference image. Organizations set match thresholds based on security needs, balancing accuracy with user convenience. |
| How can Udentify enhance facial recognition security? | Udentify provides a seamless identity verification and authentication solution, ensuring accurate and secure facial recognition while maintaining compliance with privacy standards. |
For more details on secure and efficient facial recognition solutions, visit Udentify.









