Fraud detection is the process of identifying fraudulent activities or attempts. It is important to have a detection system in place to prevent fraud from happening and to protect businesses and consumers from the financial losses that can result from these activities.
Some of the most common types of fraud include credit card fraud, identity theft, account takeover and phishing. Fraudulent activities can result in significant financial losses for businesses and consumers alike, so it is critically important to be aware of the signs of fraud and to know how to prevent it.
There are a few key things to keep in mind regarding detection capabilities. First, it is essential to have a system that can identify potential threats. This system should be able to track data and activity across all channels, including online, in-person, and over the phone.
Second, businesses and consumers should be aware of the signs of fraud. Some common signs include unexpected transactions such charges on a credit card statement, unauthorised withdrawals from a bank account, and unexpected emails or calls from someone claiming to be from a company or organisation.
Third, businesses and consumers should know what to do if they suspect fraud. If you think you may have been a victim of fraud, it is essential to report it to the proper authorities.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is fraud detection?
Fraud detection is the process of identifying whether a transaction is fraudulent or not. This can be done through various means, such as analysing customer behavior or looking for patterns in the data that might indicate fraudulent cases.
There are several ways to prevent fraud, such as using data analytics to identify risk factors, setting up detection systems, or training employees to be on the lookout for signs of fraudulent patterns. By taking preventative steps, businesses can protect themselves from financial losses and damage to their reputation.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning are increasingly being used for detection, as they can help to identify patterns and anomalies quickly and effectively.
How fraud detection works
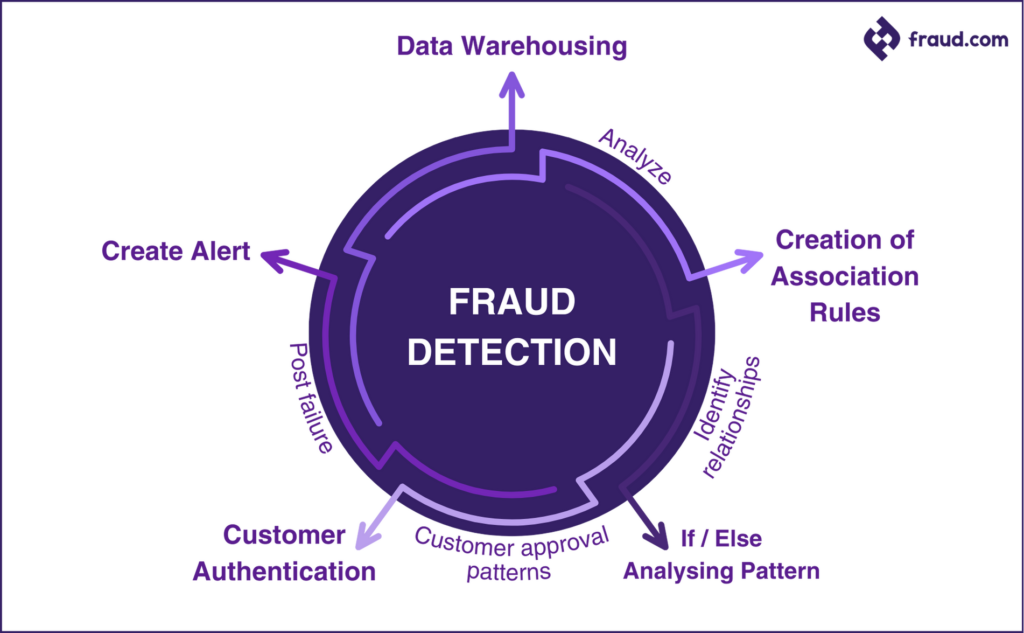
Fraud detection is a multi-stage process that involves comprehensive analysis and sophisticated techniques to identify and mitigate fraudulent activities effectively. Each stage of the process plays a crucial role in uncovering anomalies and patterns indicative of fraudulent behavior. Let’s delve into the intricacies of this process, exploring each part and its corresponding steps:
- Data Warehousing:
- Step: Analyze
- This initial stage involves the analysis of vast datasets containing transaction records, customer behaviors, and other relevant data sources. Through advanced analytics, potential fraud indicators are identified and flagged for further investigation.
- Step: Analyze
- Creation of Associate Rules:
- Step: Identify Relationships
- In this stage, algorithms are employed to establish associations and correlations within the data. By identifying relationships between variables, such as transaction amounts, frequencies, and customer demographics, potential fraud patterns are uncovered.
- Step: Identify Relationships
- If/Else Analyzing Pattern:
- Step: Customer Approval Patterns
- During this phase, sophisticated algorithms analyze customer approval patterns, distinguishing between legitimate and fraudulent transactions. By scrutinizing approval trends and deviations, suspicious activities are pinpointed for closer examination.
- Step: Customer Approval Patterns
- Customer Authentication:
- Step: Post Failure
- Following the detection of potential fraud indicators, customer authentication processes are initiated. Post-failure analysis involves verifying customer identities and scrutinizing transaction details to confirm legitimacy or identify fraudulent behavior.
- Step: Post Failure
- Create Alert:
- In the final stage, alerts are generated to notify relevant stakeholders of potential fraud instances. These alerts prompt further investigation and action, facilitating timely intervention to prevent financial losses and mitigate risks associated with fraudulent activities.
By understanding each part and step within the fraud detection process, organizations can implement robust strategies and technologies to proactively combat fraud. Lets look at how the process of fraud detection works in a visual context:
Why is fraud detection important?
Traditionally, companies have relied on fraud detection and prevention measures to mitigate financial losses and maintain positive customer relationships. However, in some jurisdictions, legislation requires the implementation of fraud prevention initiatives for businesses offering specific services, such as insurance providers in multiple US states. In the UK, a “Failure to Prevent Fraud” offense was introduced in April 2023 that holds firms liable if they benefit from employee fraud and don’t have an adequate fraud prevention program in place. Additionally, on June 7, 2023, the UK’s Payment Systems Regulator (PSR) announced a new reimbursement requirement for firms whose customers become victims of Authorized Push Payment (APP) fraud.
Fraud detection is essential for companies to safeguard their customers’ transactions and accounts by detecting fraud before or as it happens. The FBI reports that in 2022, elder fraud victims in the US lost an average of $35,101 each, resulting in a total loss of over $3 billion. In 2021, global fraud losses exceeded $55 billion, aided by technology that allows illegal funds to cross international borders.
As global awareness of fraud’s growing varieties and complexity of typologies, firms should expect the introduction of more regulation and enforcement that will impact their compliance requirements. Even if a firm is not subject to direct requirements now, fraud is a predicate offense for money laundering and may be connected to a larger pattern of criminal activity. Firms that include fraud in their overall risk management framework can better protect consumers, ensure compliance, manage loss, and fight financial crime.
Overall, understanding the following reasons why fraud detection is a very important aspect of many orgnanization’s fraud risk management strategy:
- Protecting financial assets: Fraud detection helps companies safeguard their financial assets by identifying and preventing fraudulent activities that could result in significant monetary losses.
- Maintaining customer trust: Effective fraud detection measures contribute to maintaining positive customer relationships by demonstrating a commitment to security and protecting customers from potential financial harm.
- Legal compliance: Compliance with regulatory requirements and legislation regarding fraud prevention is essential for avoiding penalties, fines, and legal liabilities.
- Preventing financial crime: By detecting and deterring fraudulent activities, companies contribute to the broader efforts to combat financial crime, including money laundering and terrorist financing.
- Mitigating reputation risks: Successful fraud detection helps mitigate reputational risks associated with security breaches or financial misconduct, preserving the company’s reputation and brand integrity.
Fraud typologies and classification
Fraud comes in various forms and can impact individuals, businesses, and entire industries. Understanding the different types of fraud is crucial for developing effective prevention and detection strategies. Fraud encompasses a wide range of deceptive practices aimed at gaining something of value through deceit or dishonesty.
Fraud can be classified based on who commits the fraudulent act:
- Internal fraud involves employees or insiders exploiting their position within an organization for personal gain.
- External fraud occurs when individuals or entities outside the organization deceive or defraud the company or its customers.
Fraud can also be classified based on the methods used by fraudsters. Common methods include identity theft, where personal information is stolen to impersonate someone else; phishing scams, where fraudulent emails or messages are used to trick individuals into revealing sensitive information; payment fraud, involving unauthorized transactions or misuse of payment instruments; and impersonation, where fraudsters pose as someone else to deceive victims.
Due to the large number and range of fraudulent activities, identifying the type of fraud being attempted in different scenarios can be a challenging task. When businesses can accurately identify fraudulent activity and stay up-to-date on the latest fraud trends, they are more prepared to protect themselves against them.
To help firms accurately identify fraud typologies, the US Federal Reserve has developed an interactive tool called the FraudClassifier Model. This model offers a user-friendly diagnostic process that categorizes fraud based on the perpetrator of the payment, the methods used to carry out the fraud, and the tactics employed. FraudClassifier’s consistent terminology and classification system acts as a lingua franca for different institutions, businesses, and fraud detection providers, enabling them to communicate current threats clearly and develop effective fraud prevention strategies.
Moreover, different industries face unique fraud challenges. In financial services, common fraud typologies include credit card fraud, money laundering, and investment scams. Healthcare fraud may involve insurance fraud, prescription fraud, or billing schemes. E-commerce fraud includes account takeover, refund fraud, and fake product listings.
Fraudsters continually adapt their tactics to exploit new opportunities. Recent trends include cryptocurrency fraud, where digital currencies are used for illicit activities; deepfake scams, involving manipulated videos or audio recordings to deceive victims; and COVID-related fraud schemes, such as fake vaccine offers or relief fund scams.
Real-world examples help illustrate the impact of fraud and the methods used by fraudsters. For instance, a case study might highlight a data breach resulting in identity theft and financial losses for thousands of individuals, or a phishing scam targeting employees of a large corporation.
Fraud can have far-reaching consequences, including financial losses, damage to reputation, legal repercussions, and emotional distress for victims. Businesses may suffer financial harm and loss of customer trust, while individuals may face identity theft, financial ruin, or other hardships.
To combat fraud effectively, organizations must implement robust prevention and detection measures. This includes investing in high-end technology to fight fraud, educating employees and customers about fraud risks, monitoring for suspicious activity, and staying informed about emerging threats and best practices in fraud prevention.
By understanding the various typologies of fraud and how they are classified, businesses and individuals can better protect themselves against fraudulent activities and minimize the impact of fraud on their lives and livelihoods.
What are common types of fraud
There are many types, but some of the most common include:
- Authorised Push Payment (APP) : This occurs when a payer is tricked into authorising a payment to a fraudulent payee. The payee may pose as a legitimate business or individual and may use phishing or other techniques to obtain the authorisation.
- Account takeover: Account takeover fraud takes place when a criminal gains access to a victim’s financial account and uses it to steal money or make unauthorised transactions. This can happen through phishing, malware, or other means.
- Phishing: This occurs when a criminal uses fraudulent emails or other communications to trick victims into revealing personal or financial information. This information can then be used to steal money or commit identity theft.
- Identity theft: Identity theft happens when a criminal obtains personal information, such as a social security number or credit card number, and uses it to commit crimes.
- Telephone or utility fraud: This occurs when a criminal poses as a representative of a legitimate business or government agency and tricks the victim into revealing personal or financial information or making unauthorized payments.
- Investment fraud: This occurs when a criminal convinces victims to invest money in a false scheme. The money may be used to fund the criminal’s lifestyle or may simply be stolen outright.
- Lottery or sweepstakes fraud: This occurs when a criminal convinces victims that they have won a lottery or sweepstakes and then asks them to pay fees or taxes to collect their prize. Often, the victim never receives the prize, and the criminal walks away with the victim’s money.
- Payment fraud: Payment fraud involves any fraudulent activity that targets payments, such as credit card fraud, where stolen card information is used to make unauthorized purchases, or check fraud, where counterfeit or stolen checks are used to make payments or withdrawals.
- Return fraud: In retail and e-commerce return fraud occurs when a criminal exploits the return process of a retailer by returning stolen or counterfeit merchandise for a refund or store credit.
- ACH (Automated Clearing House) fraud: ACH fraud involves unauthorized electronic transfers from a victim’s bank account. This can occur through various methods, such as phishing scams or malware attacks targeting online banking credentials.
- Chargeback fraud: This occurs when a consumer makes a purchase online, receives the product or service, and then falsely claims to their bank or credit card company that the transaction was unauthorized or that the product was not as described, resulting in a chargeback and a loss for the merchant.
- Insurance fraud: This involves false claims or exaggeration of damages or injuries to obtain insurance benefits or compensation.
- Employment fraud: Occurs when individuals provide false information on job applications or resumes to secure employment, or when employees engage in theft or embezzlement from their employers.
- Credit card skimming: Criminals use devices called skimmers to steal credit card information during legitimate transactions, often at ATMs or gas pumps, and then use this information to make unauthorized purchases.
- Healthcare fraud: This includes various schemes aimed at defrauding health insurance providers, such as billing for services not rendered, overcharging for services, or prescribing unnecessary treatments or medications.
- Mortgage fraud: Involves misrepresentation or omission of information on mortgage applications to obtain loans or better terms, or schemes where properties are purchased using fraudulent means.
- Investment scams: These schemes promise high returns with little risk, often targeting unsuspecting investors with promises of guaranteed profits or exclusive opportunities, but ultimately result in the loss of investment funds.
- Identity theft through data breaches: Fraudster commit identity theft by obtaininig personal information through data breaches of companies or organizations and then use this information to commit various types of fraud, including credit card fraud, tax fraud, or opening fraudulent accounts.
What’s the difference between fraud prevention and fraud detection?
Fraud prevention and fraud detection are both crucial components of a robust anti-fraud strategy, but they serve different purposes in safeguarding against fraudulent activities. Understanding the distinctions between these two concepts is essential for effectively managing fraud risks. Let’s look into some of the differences between these two essential aspect of fraud risk management:
| Aspect | Fraud prevention | Fraud detection |
|---|---|---|
| Objective | To proactively stop fraudulent activities before they occur. | To identify and mitigate fraudulent activities after they occur. |
| Timing | Implemented before fraudulent activities take place. | Implemented after fraudulent activities have taken place. |
| Focus | Focuses on implementing preventive measures and controls. | Focuses on identifying anomalies or suspicious patterns. |
| Nature of activities | Involves measures such as authentication, authorization, and education. | Involves monitoring, analysis, and investigation of transactions or behaviors. |
| Cost | Initial investment may be higher due to implementation of preventive technologies and processes. | May incur costs associated with investigation and remediation of fraud incidents. |
| Proactiveness | Takes a proactive approach to minimize fraud risks. | Reactive in nature, responding to incidents as they occur. |
| Long-term impact | Helps in building a resilient and fraud-resistant environment. | Helps in reducing losses and preventing future occurrences. |
| Examples of measures | Enhanced authentication methods, fraud training programs, transaction monitoring systems. | Fraud data analytics, anomaly detection algorithms, forensic investigations. |
By comprehensively understanding the differences between fraud prevention and fraud detection, organizations can develop a balanced approach to mitigating fraud risks and protecting their assets, reputation, and stakeholders.
What are the best methods to enhance fraud detection?
To safeguard businesses and consumers from evolving fraud risks, employing the most effective fraud detection techniques is essential. When auditing an exisiting fraud detection solution or evaluating the market for a new one, compliance professionals should consider whether the software offers most, if not all, of the following functionalities:
- Machine learning and AI: Leveraging machine learning algorithms and artificial intelligence will significantly enhance fraud detection capabilities. These technologies can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, identifying patterns and anomalies that might indicate fraudulent activities.
- Behavioral analytics: By monitoring and understanding users’ behaviors, businesses can detect deviations from normal patterns. Behavioral analytics can flag suspicious activities, such as unusual login locations, sudden changes in spending patterns, or atypical transaction amounts.
- Anomaly detection: This technique involves creating a baseline of normal behavior and flagging any data points that deviate significantly from it. Anomaly detection can uncover fraudulent transactions, unusual login attempts, or other malicious activities that do not fit typical patterns.
- Identity clustering: Grouping user identities based on common attributes and behaviors can help identify patterns of fraudulent behavior. Identity clustering can be particularly useful in detecting organized crime groups and cybercrime activities.
- Data analytics: Advanced data analytics tools can sift through large datasets and identify potential fraud indicators. By correlating information from various sources, businesses can gain valuable insights and stay one step ahead of fraudsters.
- Real-time monitoring: Detecting fraud as it happens is crucial for minimizing damages. Real-time monitoring tools can promptly identify suspicious activities, trigger alerts, and enable quick responses to mitigate the impact of fraud.
- Collaborative fraud intelligence: Sharing fraud intelligence and insights with other organizations and industry partners can lead to a more comprehensive understanding of evolving fraud tactics. Collaborative efforts enable proactive prevention and collective defense against fraudsters.
- Ongoing monitoring and updates: Fraud detection techniques should be regularly reviewed, updated, and improved to keep pace with emerging threats and vulnerabilities.
- Network analysis: Examining connections and relationships between entities, such as individuals, accounts, or transactions, can reveal patterns indicative of fraudulent activities. Network analysis can uncover hidden links between seemingly unrelated entities, facilitating the detection of complex fraud schemes.
- Geographic analysis: Analyzing the geographic locations associated with transactions or activities can help identify suspicious patterns, such as transactions originating from high-risk or unusual locations. Geographic analysis can also detect inconsistencies between reported locations and actual transaction origins.
- Device fingerprinting: Creating unique identifiers for devices used in transactions, such as computers or mobile devices, can help detect unauthorized access or suspicious activities associated with specific devices. Device fingerprinting enhances fraud detection by identifying potentially compromised or fraudulent devices.
- Biometric authentication: Implementing biometric authentication methods, such as fingerprint or facial recognition, can enhance fraud detection by verifying the identity of individuals conducting transactions. Biometric authentication adds an additional layer of security by requiring physiological characteristics unique to each individual.
- Social media analysis: Monitoring social media platforms for mentions, discussions, or indications of fraudulent activities can provide valuable intelligence for fraud detection efforts. Social media analysis can uncover information about potential fraudsters, their tactics, and their targets, enabling proactive detection and prevention of fraud.
- Transaction profiling: Creating profiles of typical transaction patterns for individual users or accounts can help detect deviations that may indicate fraudulent activities. Transaction profiling involves analyzing historical transaction data to establish baseline behavior and identify aberrations or anomalies in real-time transactions.
By incorporating these methods into fraud detection strategies, businesses can enhance their ability to identify and mitigate fraud risks effectively. Each method offers unique insights and capabilities that contribute to a comprehensive and proactive approach to fraud detection.
What are the main challenges of fraud detection
- Cost management: To keep up with the ever-expanding litany of fraud techniques and typologies, businesses may feel the need to invest in more fraud-detection tools and operations. Relying soley on rule-based transaction monitoring and fraud detection can be a challenge as scam techniques change.
- Remote transactions: Business is increasingly carried out without physical interaction taking place. While this is convenient and cost-effective, it also opens the door for fraudsters to impersonate genuine customers or intercept their details.
- Speed of transactions: Today’s transaction ecosystem is built for speed and convenience. Even a relatively complex process like a loan application can be carried out via smartphone, while more routine purchases are completed in a few keystrokes. This high-speed, low-friction environment can make it easy for fraudsters to complete their crimes and disappear before they can be detected.
- False positives: A fraud detection system that is over-zealous can lead to higher false positives. This is inconvenient for customers, who may become less loyal as a result, and expensive for businesses, who must expend time and resources following up the alert.
- Range of transaction types: A huge number of tools and services are now used to move money around, from payment apps and cryptocurrency trading platforms to traditional loans, credit cards, and savings accounts. The proliferation of digital financial services in particular creates multiple potential access points for fraudulent actors.
- Evolution of Fraud Techniques: Fraudsters continuously evolve their tactics to evade detection, posing a constant challenge for fraud detection systems to keep pace with emerging threats and sophisticated techniques.
- Globalization and Cross-Border Transactions: The interconnected nature of global commerce presents challenges in detecting and preventing fraud across borders, where regulatory differences, jurisdictional issues, and varying levels of security measures complicate efforts to combat fraud effectively.
- Data Privacy and Compliance: Striking a balance between effective fraud detection and respecting data privacy regulations poses challenges for businesses, as stringent compliance requirements may limit access to data crucial for detecting fraudulent activities.
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach that integrates advanced technologies, robust analytics, and collaboration among stakeholders to stay ahead of fraudsters and protect against financial losses and reputational damage.
Applications of fraud detection services
Detection services are used to detect fraud such as identity theft and credit card fraud, they can also help to prevent money laundering and phishing. Fraud detections systems are commonly used by the following industrie:
Banking & financial services – Detection Services are used in the banking and financial services industry to identify and prevent fraudulent activities such as money laundering and credit card fraud. The services use data analytics and machine learning algorithms to detect fraudulent patterns and transactions. When a fraudulent transaction is detected, the service immediately alerts the bank or financial institution so that they can take appropriate action.
Ecommerce & online retail businesses – When customers make online purchases, they typically provide their credit card or other personal information. Fraudsters can use this information to commit identity theft or other fraudulent activities. Detection services use data analytics and machine learning algorithms to detect patterns and suspicious transactions. If a fraudulent transaction is detected, the system alerts the ecommerce organization.
Gaming industry – The gaming industry is susceptible to threats due to a large amount of money involved. Fraudsters may attempt to hack into accounts to steal virtual currency or items, or they may create fake accounts to defraud other players.
IT and telecom industry – The IT and telecom industry is also susceptible to fraud. Fraudsters may attempt to hack into accounts or systems to steal sensitive data, or they may create fake accounts to defraud customers. There are many types of fraud that can occur in the IT and telecom industry, so businesses must have a detection system in place.
Crypto Markets – As the popularity of crypto assets increases, fraudsters have managed to steal large amount of crypto assets, including cryptocurrencies and NFTs. Crypto fraud and scams are of big concern especially as users personal data and identities can easily be stolen, therefore crypto exchnages and other DeFi organisations should consider using strong identity verification and authentication on top of an effective fraud detection system.
How fraud detection works – Data analysis detection techniques
Many different techniques can be used for detection, depending on the type of fraud being committed and the transactions involved. Data Analysis detection techniques fall under two classes, statistical techniques and artificial intelligence:
Statistical data analysis methods used to detect fraud
The following methods use mathematical and statistical techniques to identify patterns in data that may be indicative of fraud. These can be used to identify unusual patterns in financial transactions, customer behavior, or other types of data.
- Calculating statistical parameters: This approach calculates certain statistical parameters, like means, medians, and standard deviations, from a dataset. These parameters can then be used to identify outliers or unusual values that may be indicative of fraud.
- Regression analysis: This approach uses regression analysis to identify relationships between different variables in a dataset. This can be used to identify variables that are predictive of fraud or to find clusters of data that are more likely to be fraudulent.
- Probability distributions and models: This approach uses probability theory to model the likelihood of fraud occurring. This can be used to identify which transactions are more likely to be fraudulent or to predict the probability of threats occurring in future transactions.
- Data matching This approach compares data from different sources to look for matches or discrepancies that may be indicative of fraud. This can be used to match transaction data with customer data to identify fraudulent transactions or to match data from different financial institutions to identify laundering activity.
AI techniques used to detect fraud
Did you know that Artificial Intelligence (AI) can help prevent and detect fraud by uncovering trends? Many different AI techniques can be used for detection, including data mining, predictive modelling, and anomaly detection. Check them out below.
- Data mining: Data mining is a process of extracting patterns from data. It can be used to detect fraud by finding unusual patterns in data that may be indicative of fraud. The patterns found in data mining can be used to create predictive models that can be used for future detection, too. When data mining for fraud, common data sets that are analyzed include transaction data, customer data, and product data.
- Neural networks: Neural networks are a machine learning algorithm that can be used for predictive modeling. Neural networks can learn to detect patterns in data that are indicative of fraudulent activities. Once a neural network has been trained to detect these patterns, it can be used to predict whether new data is likely to be fraudulent or not.
- Machine Learning: Machine learning is a type of artificial intelligence used for predictive modeling. Machine learning algorithms can learn from data to detect patterns that are indicative of fraud. Once a machine learning algorithm has been trained to detect these patterns, it can be used to predict whether new data is likely to be fraudulent or not.
- Pattern recognition: Pattern recognition is a process of identifying patterns in data. It can be used by looking for anomalies in transaction data. Many different algorithms can be used for pattern recognition, including neural networks and support vector machines.
- Face recognition : Face recognition is a form of biometric authentication that can be used to detect fraudulent behaviour. It compares a person’s facial features to a database of known faces. If there is a match, the person is authenticated. If there is no match, the person is not authenticated.
- Liveness detection: Liveness detection is a process of verifying that a person is actually present at the time of authentication. It can be used to detect and prevent fraudulent behaviours such as identity theft by making sure that the person being authenticated is the person they claim to be. There are many liveness detection algorithms, including facial recognition and iris recognition.
What are the benefits of fraud detection for organisations?
Organisations can benefit from fraud detection in many ways, including:
- Reduced losses from fraud: Fraud detection can help organisations to identify and prevent fraud before it occurs, minimising losses from fraudulent activity.
- Improved reputation: Organisations taking steps to detect and prevent fraud are likely to have a better reputation with customers and the general public, and less customer friction overall.
- Greater security: Fraud detection can help organisations to improve their security by identifying potential security risks and taking steps to mitigate them.
- Improved decision-making: Organisations that can detect and prevent fraud are likely to be able to make better decisions about how to allocate resources and manage risks.
- Improved efficiency: Organisations that can detect and prevent fraud are likely to be more efficient in their operations, as they will be able to avoid wasting time and resources on investigating and prosecuting fraudulent activity.
- Robust internal controls: Fraud detection can help organisations identify and correct weaknesses in their internal controls, which can help to prevent future fraud.
- Greater compliance: Organisations that can detect and prevent fraud are likely to comply with laws and regulations related to fraudulent behaviour.
Why should companies use AI for fraud management and detection?
There are many reasons why companies should use AI for fraud management and detection.
AI can help companies to automate fraud detection processes, which can save time and money. AI can also help companies to identify patterns in data that may be indicative of fraud. Additionally, AI can help companies to monitor customer behaviour and transactions in real-time, which can help to prevent fraudulent activities before they occur. The use of AI can also help companies to investigate fraud after it has occurred by providing insights that may not be readily apparent.
Regarding fraud detection, AI can provide several advantages over traditional methods. AI can help to speed up the process of detecting fraud, as it can analyse large amounts of data much faster than a human can. Additionally, AI can help to identify patterns in data that may be indicative of fraud.
Applications of fraud detection
Fraud detection coupled with AI finds utility across various sectors, helping mitigate fraudulent risks and safeguard assets. Below are sector-based applications:
- Banking and finance:
- Identification of fraudulent transactions, including credit card fraud and money laundering.
- Detection of unauthorized access to accounts or identity theft.
- Monitoring of loan applications to prevent fraudulent submissions.
- Healthcare:
- Detection of fraudulent insurance claims, such as billing for services not rendered or unnecessary medical procedures.
- Monitoring prescription patterns to identify doctor shopping or drug diversion.
- Prevention of identity theft for medical services.
- E-commerce:
- Detection of fraudulent orders, including stolen credit card information or fake identities.
- Monitoring of user behavior to identify suspicious activities, such as account takeover or fake reviews.
- Prevention of refund fraud and chargeback abuse.
- Telecommunications:
- Identification of subscription fraud, where individuals use false identities to obtain services.
- Detection of call detail record (CDR) manipulation to inflate usage or evade billing.
- Monitoring of roaming patterns to identify SIM card cloning or fraudulent usage.
- Insurance:
- Detection of fraudulent claims, including exaggerated damages or staged accidents.
- Monitoring of policyholder behavior to identify patterns indicative of fraud.
- Prevention of identity theft for insurance purposes, such as falsified medical records.
- Government and public services:
- Detection of fraudulent benefit claims, such as unemployment or welfare fraud.
- Monitoring of tax filings to identify false deductions or unreported income.
- Prevention of identity theft for government services, such as fraudulent use of social security numbers.
- Cryptocurrency:
- Identification of fraudulent transactions, including pump-and-dump schemes and ICO scams.
- Monitoring of wallet addresses to track illicit activities such as ransomware payments or money laundering.
- Detection of fraudulent ICOs and token sales, preventing investors from falling victim to Ponzi schemes or fraudulent projects.
Fraud detection systems leverage advanced algorithms and data analytics to sift through large volumes of data, flagging anomalies and patterns indicative of fraudulent activity. These applications play a crucial role in safeguarding assets, protecting consumers, and maintaining the integrity of various sectors.
How can AI fraud detection tools help fight fraud?
There are many different AI detection tools available to help businesses fight fraud. Some of these tools use machine learning to identify patterns in data that may indicate fraud, while others use natural language processing to analyse text data for clues about potential fraudulent threats. Still, other AI detection tools use a combination of these techniques to provide a more comprehensive detection approach.
Fighting fraud is an important part of doing business, and AI detection tools can help businesses to identify and prevent fraud before it occurs. By using these tools, businesses can save time and money that would otherwise be lost to fraud, and they can protect their reputation by ensuring that their customers are not left feeling cheated or taken advantage of.
Frequently asked questions about fraud detection
Navigating the landscape of fraud detection can raise many questions for businesses and individuals alike. Here are answers to some common inquiries:
- What is fraud detection?
- Fraud detection is the process of identifying and mitigating fraudulent activities or attempts within a system or organization. It involves monitoring transactions, behaviors, and patterns to detect anomalies or suspicious activities indicative of fraud.
- Why is fraud detection important?
- Fraud detection is crucial for protecting businesses, consumers, and financial institutions from financial losses, reputational damage, and legal liabilities associated with fraudulent activities. It helps prevent fraudsters from exploiting vulnerabilities and safeguards assets and sensitive information.
- What are the main challenges of fraud detection?
- Some of the main challenges of fraud detection include managing costs, addressing remote transactions, dealing with the speed of transactions, minimizing false positives, adapting to the range of transaction types, staying ahead of evolving fraud techniques, managing globalization and cross-border transactions, and ensuring compliance with data privacy regulations.
- How does fraud detection work?
- Fraud detection works by analyzing data from various sources, such as transaction records, customer behaviors, and external factors, to identify patterns, anomalies, or red flags indicative of fraudulent activities. It often involves the use of advanced technologies, algorithms, and analytics to automate the detection process and improve accuracy.
- What are some common fraud detection techniques?
- Common fraud detection techniques include machine learning and AI, behavioral analytics, anomaly detection, identity clustering, data analytics, real-time monitoring, collaborative fraud intelligence, network analysis, geographic analysis, device fingerprinting, biometric authentication, and social media analysis.
- How can businesses enhance their fraud detection capabilities?
- Businesses can enhance their fraud detection capabilities by investing in advanced technologies, implementing robust fraud prevention measures, training employees on fraud awareness, collaborating with industry partners, regularly updating and improving fraud detection systems, and staying informed about emerging fraud trends and techniques.
- What are the potential consequences of ineffective fraud detection?
- Ineffective fraud detection can lead to financial losses, reputational damage, regulatory penalties, loss of customer trust, and legal liabilities for businesses. It can also result in increased fraud risk exposure and higher operational costs associated with fraud investigation and remediation efforts.
- How can individuals protect themselves from fraud?
- Individuals can protect themselves from fraud by being vigilant about their financial accounts and transactions, monitoring their credit reports regularly, using strong and unique passwords, avoiding sharing sensitive information online or over the phone, and staying informed about common fraud schemes and scams.
Our fraud detection solution – aiReflex

aiReflex is a state-of-the-art AI-driven detection solution that is used to detect and prevent fraud in real-time. aiReflex is powered by deep learning algorithms constantly learning and evolving to keep up with the latest fraud trends and patterns.
aiReflex is used by leading banks, e-commerce companies, and online businesses to detect and prevent fraud. The solution is used to identify and flag suspicious activities, such as account takeover, identity theft, and other fraud scenarios. aiReflex is an accurate, flexible and powerful mechanism that efficiently reduces fraud and improves customer trust. You can check it out here.









