The cost of fraud is on the rise, and so are the stakes. The National Crime Agency (NCA) estimates fraud losses to the UK at around £190 billion every year. Each year new fraud trends arise as fraudsters adopt new techniques to defraud people across all industries.
As the cost of fraud continues to soar, businesses are looking for new ways to protect their data by adopting effective fraud prevention techniques. One promising solution is biometric authentication when authenticating real users.
In this article, we’ll explore biometric authentication in depth. We’ll cover what it is, how it works, and the many business types that can benefit from this technology.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication is a form of identity authentication that uses biological traits to confirm someone’s identity. It is a method used for Passwordless Authentication. It is often used as an alternative to traditional methods like passwords or PIN numbers. That’s because biometric data is unique to everyone, making it much harder for fraudsters to counterfeit.
The biometric technology authentication has come a long way since itsintroduction in the 1970s. Today, biometric authentication can be used to authenticate a person’s identity in real time and with a high degree of accuracy. As a result, biometric authentication is becoming an increasingly popular way to protect data and prevent fraud.
Its advantages make it a technology worth considering for any business that collects and stores sensitive customer data. As more businesses recognise the need for stronger security, biometric authentication is likely to become even more common.
How does Biometric authentication work?
For biometric authentication to take place, an identity verification process must have been completed previously.
There are four main steps in the biometric authentication process. Let’s take a closer look at each:
- Enrolment
In this step, biometric data is collected from an individual and stored in a database. This data is initially collected through the identity verification process using a variety of devices, including scanners, cameras, and microphones. For instance, fingerprints can be collected using a finger scanning device, and facial biometrics are captured with the camera of a smartphone.
- 2. Processing and analysis
Once the biometric data has been collected, it must be processed and analysed. This step is important for ensuring that the biometric data is of high quality and authentic and can be used to accurately authenticate someone’s identity with the identity data that was previously verified, making sure that the biometric data matches the one previously verified.
- 3. Comparison
In this step, the biometric data is compared to a reference template. This template can be stored in the same database as the biometric data or in a separate location. The reference template is used to confirm that the biometric data belongs to the individual being authenticated.
- 4. Decision
Once the biometric data has been compared to the reference template, a decision is made. This decision is based on the similarity between the biometric data and the reference template. If the biometric data matches the reference template, then the individual’s identity is confirmed. If not, then authentication fails.
What is biometrics?
Biometrics refers to the measurement and statistical analysis of people’s unique physical and behavioral characteristics. These characteristics are used to verify their identity or authenticate their access to various systems, devices, or data. Biometric systems are designed to provide a higher level of security compared to traditional methods like passwords or PINs.
Three types of biometric security
Biometric security uses unique physical or behavioural traits for identity verification. Three widely-used methods include fingerprint recognition, facial recognition, and voice recognition. Each offers distinct advantages in accuracy and security, making them essential in modern authentication systems. Let’s explore these biometric types in detail.
- Fingerprint recognition: Biometric fingerprint authentication relies on capturing and analyzing the unique patterns of ridges and valleys present on an individual’s fingertips. This method is widely used due to its accuracy and ease of implementation in various devices, such as smartphones and access control systems.
- Facial recognition: Facial biometrics involves analyzing facial features such as the distance between the eyes, nose shape, and jawline to identify individuals. It is commonly used in surveillance, access control, and authentication applications, offering both convenience and security.
- Voice recognition: Voice biometrics uses the unique characteristics of an individual’s voice, such as pitch, tone, and pronunciation, to verify their identity. Voice recognition systems are increasingly being used in call centers, banking, and other industries where secure authentication is essential. This technology provides a convenient and secure method of authentication, especially in scenarios where other biometric modalities may not be feasible.
The importance of biometric authentication technology
Adopting Biometric Authentication Technology is a key part of Identity Verification. Once a user’s identity is verified with their specific biometrical characteristics, every time they access their account and information, they should be authenticated using the same biometrical characteristics. This would help prevent fraud such as identity theft and identity fraud, and other known fraud scenarios such as account takeover fraud.
When Biometric Authentication is used with other techniques such as liveness detection, it becomes impossible to spoof the biometrics of the authentic users. With liveness detection, fraudulent methods used to spoof someone’s identity such as 3D masks or deepfakes would not bypass the biometric checks if the user isn’t using their live face or other live biometrics to authenticate themselves.
What are the use cases of biometric authentication?
Biometric authentication has become indispensable across industries. It ensures both heightened security and convenience in various scenarios, from law enforcement to healthcare and beyond. With its integration, biometric authentication finds applications across a wide range of industries and sectors, offering enhanced security and convenience in various scenarios.
Law enforcement
Biometric authentication is extensively used in law enforcement for criminal identification and investigation purposes. Law enforcement agencies use biometric data such as fingerprints, facial features, and even DNA to match individuals to criminal records or identify suspects in surveillance footage.
Travel
In the travel industry, biometric authentication streamlines the passenger experience by enabling fast and secure identity verification at various checkpoints, including airport security, immigration, and boarding gates. Biometric technologies such as facial recognition and iris scanning are increasingly integrated into automated border control systems, enhancing both security and efficiency.
Healthcare
Biometric authentication plays a crucial role in ensuring secure access to sensitive healthcare information and medical facilities. Healthcare providers use biometrics to authenticate patients, access electronic medical records, and prevent unauthorized access to healthcare data, thus safeguarding patient privacy and confidentiality.
Identity and access management systems
Biometric authentication is widely adopted in identity and access management systems across industries. It provides a reliable method of authenticating users and granting access to digital resources, networks, and physical premises based on their unique biometric traits. This enhances security by reducing the reliance on easily compromised passwords or access cards.
Payments
Biometric authentication is revolutionizing the payments industry by offering secure and convenient methods of verifying transactions. Biometric technologies such as fingerprint and facial recognition enable users to authenticate payments using their unique biological traits, reducing the risk of fraud and providing a seamless checkout experience both online and in-store.
Border control and immigration
Biometric authentication is employed by border control and immigration authorities to enhance security and streamline the entry and exit processes at borders and ports of entry. Biometric data, such as fingerprints and facial images, are collected and matched against databases to verify travelers’ identities, detect fraud, and facilitate secure border crossings.
Employee time and attendance tracking
Biometric authentication systems are used in workplaces to accurately track employees’ time and attendance. Biometric modalities such as fingerprint or facial recognition enable employees to clock in and out securely, preventing time theft and ensuring accurate payroll processing.
Education
Biometric authentication is increasingly used in educational institutions for student attendance tracking, access control to secure areas, and securing exam processes. Biometric systems help prevent unauthorized access to sensitive areas and ensure the integrity of academic assessments.
These diverse use cases highlight the versatility and effectiveness of biometric authentication in enhancing security, efficiency, and user experience across various industries and sectors.
What are the types of biometric authentication?
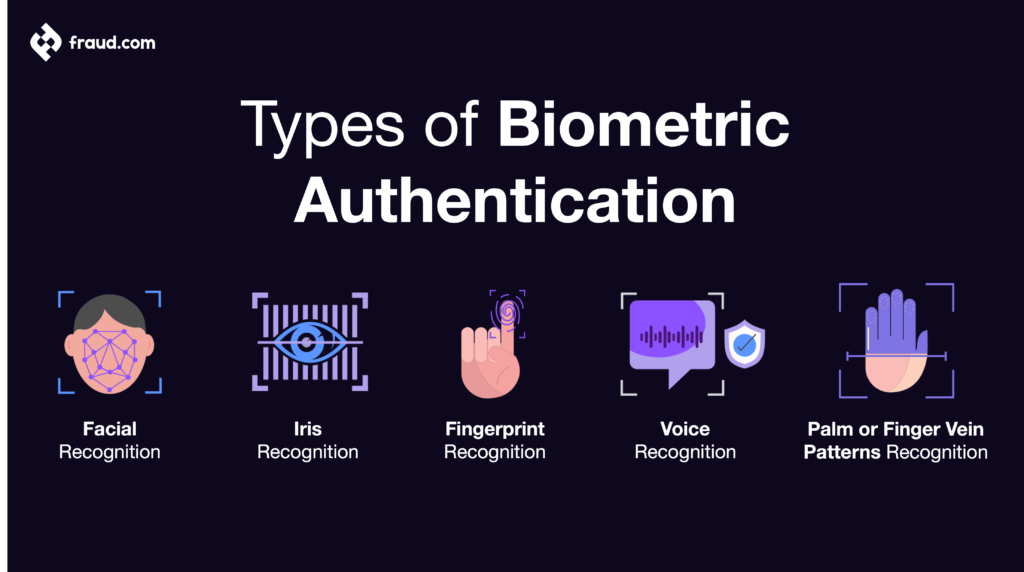
There are several different types of biometric authentication. The most common types are listed below.
Facial recognition
Face recognition technology uses an individual’s unique facial features to confirm their identity. This type of biometric authentication is often used in security systems, as it can be used to quickly and accurately authenticate someone’s identity in real time.
In recent times facial recognition technology has become much more accurate, thanks to advances in machine learning and artificial intelligence to prevent fraud such as identity fraud.
Iris recognition
Iris recognition is a type of biometric authentication that uses an individual’s unique iris pattern to confirm their identity. This type is very accurate and is often used in high-security biometric systems.
One advantage of iris recognition is that it can be used from a distance. This means that iris recognition can be used for security purposes without the need for physical contact.
Fingerprint recognition
Fingerprint recognition is a type of biometric authentication that uses an individual’s unique fingerprint to confirm their identity. This type of biometric authentication is often used in security systems as it is quick and accurate.
One advantage of fingerprint recognition is that it can be used in a variety of situations. For instance, fingerprint recognition can be used to unlock a smartphone or to log into a computer.
Voice Recognition
Voice recognition is a type of biometric authentication that uses an individual’s unique voice to confirm their identity. This type of biometric authentication is often used in security recognition systems, thanks to its quickness and accuracy. Voice recognition is difficult to spoof.
Palm or finger vein patterns
Another increasingly popular biometric identification method is scanning an individual’s palm or finger veins. This method works by shining near-infrared light on the skin, which makes the veins underneath visible. The vein pattern is then captured by a camera and used to confirm the individual’s identity.
Like other biometric authentication methods, palm vein recognition is quick and accurate.
Biometric authentication and identification
Biometric technology serves two primary functions within the realm of security: authentication and identification. While both processes adopt unique biological traits for verification purposes, they differ in their specific applications and methodologies.
Biometric authentication
Biometric authentication involves the verification of an individual’s identity based on their unique physiological or behavioural characteristics. This process compares biometric data captured from an individual, such as fingerprints, facial features, or voice patterns, against stored templates in a database. If the captured biometric data matches the stored template within an acceptable threshold of similarity, the individual is granted access or authentication.
Biometric authentication is commonly used in scenarios where secure access control is paramount, such as unlocking smartphones, accessing sensitive data or systems, and authenticating financial transactions. By relying on biometric traits that are inherently unique to each individual, biometric authentication provides a robust and reliable method of identity verification, enhancing security and convenience.
Biometric identification
Biometric identification, on the other hand, involves the process of matching captured biometric data against a database of multiple records to identify or establish the identity of an individual. Unlike authentication, which verifies whether an individual is who they claim to be, biometric identification aims to determine the identity of an individual based solely on their biometric characteristics.
Biometric identification is commonly used in scenarios where the identity of an individual needs to be established from a pool of potential matches, such as law enforcement applications, border control, and national identification programs. By comparing biometric data against a large database of records, biometric identification enables authorities to accurately identify individuals, track suspects, and prevent identity fraud or impersonation.
In summary, biometric authentication verifies an individual’s identity for access or authentication purposes, while biometric identification aims to establish the identity of an individual from a pool of potential matches. Both processes leverage the unique characteristics of individuals to enhance security, streamline processes, and mitigate the risk of identity-related fraud or breaches.
In which business types can biometric authentication be used?
Biometric authentication can be used in just about any type of business. Here are a few examples:
- Gaming
Given how big the gaming industry is, it’s no surprise that it’s a major target for hackers. Biometric authentication can help gaming companies protect their customers’ data and prevent fraud. It can also be used to verify the identity of gamers and to prevent cheating.
For instance, biometric authentication can be used to unlock game content or to make in-game purchases. Thus, if you’re a gaming company, biometric authentication is definitely something to consider.
- Cryptocurrency
Cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin and Ethereum have become increasingly popular in recent years. As the value of these currencies has gone up, so has the risk of crypto fraud. In 2021 alone, scammers made away with $14 billion in cryptocurrency. And the threat is only getting bigger.
That’s where biometric authentication comes in. By using biometric authentication, cryptocurrency companies can authenticate the identity of their users and prevent fraud. For instance, it be used to authenticate the identity of users when they make a transaction, such as withdrawing their crypto funds.
- Insurance
The insurance industry is another business that can benefit from biometric authentication. Insurance companies can use biometric authentication to verify the identity of customers and prevent fraud. For instance, when a client calls to make a claim, biometric authentication can be used to verify their identity. This would help to prevent fraudsters from making false claims.
- Finance
An estimated 71% of all cases of breaches are motivated by financial gain. It thus follows that financial institutions are among the businesses that are most at risk of being targeted by cybercriminals.
Biometric authentication can help financial institutions protect themselves and their customers. For instance, biometric authentication can be used to authenticate the identity of customers when they make a transaction. This would help to prevent fraudsters from making unauthorised transactions.
- Healthcare
Any healthcare organisation that deals with sensitive patient data is at risk of being hacked. Therefore, biometric authentication is becoming increasingly popular in the healthcare industry. Biometric authentication can help healthcare organisations verify the identity of their employees and prevent unauthorised access to patient data.
Benefits of biometric authentication for enterprise security
Biometric authentication offers a multitude of advantages for enhancing enterprise security and streamlining operational processes.
1. Restricts access
Biometric authentication enables organizations to restrict access to sensitive areas, devices, and data only to authorized personnel. By relying on unique biological traits for verification, biometric systems significantly reduce the risk of unauthorized access or breaches.
2. Records timeliness
Biometric authentication systems record the time and attendance of employees with precision and accuracy. This data can be invaluable for tracking employee hours, ensuring compliance with labor regulations, and identifying any discrepancies or irregularities.
3. Enhances security measures
Compared to traditional authentication methods like passwords or PINs, biometric authentication offers a higher level of security. Biometric traits such as fingerprints or facial features are difficult to replicate, reducing the likelihood of unauthorized access or identity theft.
4. Replaces passwords
Biometric authentication eliminates the need for passwords, which are vulnerable to hacking, phishing, or unauthorized disclosure. By replacing passwords with biometric verification, organizations can strengthen their security posture and mitigate the risk of password-related breaches.
5. Minimizes human error
Biometric authentication minimizes the potential for human error in authentication processes. Unlike passwords or access cards, which can be forgotten, lost, or stolen, biometric traits are inherently tied to the individual and cannot be easily misplaced or forgotten.
6. Eases installation
Modern biometric authentication systems are designed to be user-friendly and easy to install. With advancements in technology, organizations can seamlessly integrate biometric solutions into their existing infrastructure without significant disruption to operations.
7. Offers reasonable costs
While biometric authentication systems may have upfront costs for implementation, they often offer long-term cost savings compared to traditional security measures. By reducing the need for password resets, mitigating the risk of security breaches, and streamlining operational processes, biometric authentication provides a cost-effective security solution for enterprises.
These benefits highlight the value of biometric authentication in bolstering enterprise security, enhancing operational efficiency, and mitigating security risks.
Advantages of biometric authentication
The use of traditional authentication methods like passwords and PINs is still very common. However, biometric authentication is quickly becoming the preferred method of authentication for many people and businesses. This is because biometric authentication has several advantages over traditional methods. Here are some of them:

- Accuracy
Perhaps the main advantage of biometric authentication is that it is more accurate than traditional methods. This is because biometric authentication uses physical or behavioural characteristics that are unique to everyone. This makes it much harder for someone to impersonate another person.
- Convenience
Any superior authentication method must be convenient, or else people will simply not use it. Biometric authentication is more convenient than traditional methods because it doesn’t require you to remember a password or carry a physical token. All you need is your biometric data.
- Speed
Another advantage of biometric authentication is that it is much faster than traditional methods. This is because biometric information can be captured and processed quickly. Traditional methods like passwords and PINs, on the other hand, often require you to input a large amount of data, which can take time.
- Cost-effectiveness
Biometric authentication is more cost-effective than traditional methods in the long run. This is because biometric data can be stored electronically and reused again and again. Traditional methods like passwords and PINs, on the other hand, often must be changed frequently, which can be costly.
Our biometric authentication solution – Udentify
Now that you know more about biometric authentication and its advantages, you might be wondering how you can implement it in your business. Luckily, there’s no need to start from scratch. Udentify offers a biometric authentication solution that is accurate, convenient, fast, and cost-effective.
With Udentify, you get to authenticate the real identity of people in just seconds. Whether it’s your customer, employee, user, business partner, student, or patient, you can be sure that you’re dealing with the right person.
What’s more, Udentify is easy to use and integrates seamlessly with your existing systems. There’s no need to make any major changes to your infrastructure. You can start using Udentify right away. With Udentify’s six layers of security, preventing fraud has never been this easy.
Discover the power of biometric authentication today!
As fraud increases, businesses are increasingly turning to biometric authentication to protect themselves. This is because biometric authentication is more accurate, convenient, and cost-effective than traditional methods. If you’re looking for a better way to authenticate the identity of your employees or customers, biometric authentication is worth considering.
Ready to get started? Check out Udentify today and discover a new era of identity verification, authentication, and fraud prevention.









