Digital transformation is reshaping how we handle money and share personal information and the financial world has become both vast and complex. For businesses operating in this space, the challenge of staying ahead of fraud while meeting compliance demands has grown increasingly urgent. Enter Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations, a cornerstone of modern financial security and a critical tool in the fight against fraud. By rigorously verifying identities and closely monitoring customer behavior, KYC acts as a powerful deterrent to fraudulent schemes.
Beyond its role in fraud prevention, KYC also helps organizations stay on the right side of regulatory requirements, fostering trust with both authorities and customers. This article takes a closer look at how Know Your Customer regulations are shaping the security of financial systems, underscoring their vital role in preventing fraud and ensuring compliance. Together, we’ll examine how strong KYC practices not only protect businesses from risk but also enable them to grow with confidence in an increasingly risk-aware environment.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is KYC?
Know Your Customer (KYC) is a critical process employed by financial institutions and various businesses to verify the identity of their clients. Beyond merely collecting information, KYC ensures that the individuals or entities a business engages with are who they claim to be. This identity verification mechanism is foundational in detecting and mitigating risks associated with fraudulent activities and illicit financial transactions.
KYC involves a meticulous assessment that includes gathering personal data, verifying government-issued IDs, and understanding the nature of the customer’s activities. By establishing a strong KYC process, businesses not only safeguard against financial crimes but also build trust and confidence among their clients. This strengthens relationships while meeting legal and ethical obligations
What are KYC regulations? Breaking down the basics
KYC regulations are a series of standardized rules set by regulatory bodies across the globe to ensure businesses properly identify and verify their customers. These rules are designed to tackle financial crimes like money laundering, terrorism financing, and fraud. At their heart, KYC regulations require companies to perform detailed checks before bringing on new clients and to continuously monitor their activities.
This process typically unfolds in three main stages: the Customer Identification Program (CIP), which confirms a customer’s identity; Customer Due Diligence (CDD), which assesses their risk level; and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD), which applies stricter scrutiny to high-risk individuals or entities. While the core principles of KYC are consistent worldwide, the specifics can vary depending on local laws and industry requirements. By following these regulations, businesses not only stay compliant but also play a crucial role in protecting the global financial system from illicit activities.
Why are KYC regulations important in today’s financial landscape?
In today’s fast-paced, digitally-driven world, the financial system is more interconnected than ever, but it’s also more vulnerable to risks like fraud, money laundering, and cybercrime. KYC regulations have become a cornerstone of financial security, helping businesses navigate these challenges effectively. Here’s why they matter:
- Combatting money laundering and terrorism financing: KYC regulations act as a critical line of defense, making it harder for criminals to exploit financial systems for illegal activities. By requiring thorough identity verification, they ensure that illicit funds can’t easily flow through legitimate channels.
- Building trust and transparency: By verifying customer identities and monitoring transactions, KYC fosters trust between businesses and their clients. This transparency strengthens relationships and helps organizations maintain a reputation for integrity and accountability.
- Avoiding costly penalties and fines: Non-compliance with KYC regulations can lead to severe financial and legal consequences. Staying compliant not only helps businesses avoid hefty fines but also protects them from reputational damage.
- Enhancing security in a digital world: With identity theft and cyber fraud on the rise, KYC processes provide a vital layer of protection. By leveraging technologies like biometrics and AI, they help detect and prevent fraudulent activities before they cause harm.
- Supporting global financial stability: KYC regulations contribute to the integrity of the global financial system by ensuring that businesses operate responsibly. This helps create a safer, more secure environment for everyone.
- Enabling risk-based decision making: Through Customer Due Diligence (CDD) and Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD), KYC allows businesses to assess and manage risks effectively. This ensures that high-risk customers are identified and monitored closely.
- Adapting to Regulatory Evolution: As financial regulations evolve, KYC helps businesses stay ahead of the curve. It ensures they remain compliant with changing laws and industry standards, reducing the risk of legal complications.
In short, KYC regulations are essential for maintaining security, building trust, and ensuring compliance in today’s complex financial landscape. They empower businesses to operate confidently while safeguarding the broader financial ecosystem.
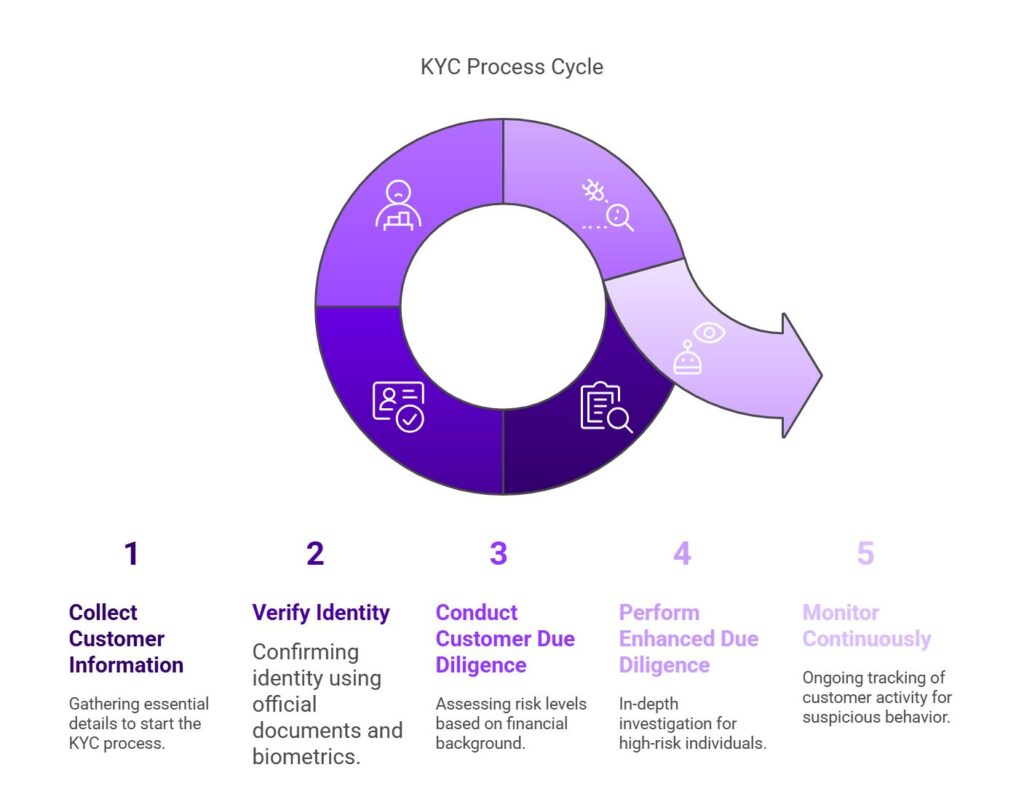
KYC requirements
Know Your Customer (KYC) requirements are a critical part of fraud prevention, helping financial institutions and other businesses verify customer identities and prevent financial crimes. These guidelines ensure companies follow a structured process to collect and authenticate customer information, allowing only legitimate individuals to access financial services. Businesses that understand and implement KYC effectively stay compliant and protect themselves from fraud.
Collecting customer information
KYC compliance starts with gathering essential customer details—full name, date of birth, address, and identification numbers. This information lays the groundwork for identity verification. Accuracy is key; incomplete or incorrect data can lead to compliance failures and security risks.
Verifying identity
After collecting basic details, businesses must confirm a customer’s identity using official documents like passports, driver’s licenses, or government-issued IDs. Many organizations now integrate biometric authentication, fingerprints, facial recognition, or voice verification, to improve security and reduce fraud.
Conducting Customer Due Diligence (CDD)
Customer Due Diligence (CDD) assesses a customer’s risk level by analyzing their financial background, transaction patterns, and overall risk profile. Businesses use this process to flag high-risk individuals who may require additional scrutiny.
Performing Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD)
For customers identified as high-risk, Enhanced Due Diligence (EDD) goes a step further. This involves a deeper investigation into the source of funds, closer transaction monitoring, and an evaluation of any affiliations that may raise concerns. EDD helps businesses mitigate financial threats and remain vigilant in high-risk scenarios.
Monitoring continuously
KYC isn’t a one-time requirement, it’s an ongoing process. Businesses must continuously track customer activity to detect suspicious behavior and prevent fraud. With the help of advanced technology, companies can automate this process, identifying risks in real time and responding swiftly.
By embedding these KYC practices into daily operations, businesses don’t just comply with regulations, they strengthen their defenses against fraud and create a safer environment for customers and themselves.
What is KYC verification?
KYC verification is a key step in the Know Your Customer process, confirming that a customer is who they claim to be. It plays a crucial role in preventing fraud and ensuring financial institutions operate with integrity while staying compliant with regulations.
KYC verification involves a series of checks to validate a customer’s identity. Businesses compare the personal information provided by customers against reliable sources to confirm accuracy. The goal is to authenticate identities without creating unnecessary friction in the customer experience.
Key components of KYC verification
- Document verification – Customers submit official documents like passports, driver’s licenses, or national IDs. Businesses examine security features such as watermarks, holograms, and expiration dates to confirm authenticity.
- Biometric verification – Many organizations enhance security by incorporating biometric checks, such as fingerprint scans, facial recognition, or voice authentication. Since these traits are unique, they add an extra layer of protection against identity fraud.
- Database checks – Businesses cross-reference customer details with watchlists, politically exposed persons (PEP) lists, and sanction databases to flag individuals who may pose a higher risk.
- Address verification – Companies confirm customers’ addresses by reviewing utility bills, bank statements, or other reliable documents to ensure the information is up to date.
By integrating these verification steps, businesses not only comply with regulations but also build a stronger defense against fraud while maintaining a seamless customer experience.
KYC compliance
KYC compliance ensures that businesses follow legal and regulatory requirements when verifying customer identities. It helps prevent fraud, money laundering, and other financial crimes while keeping companies in line with global standards.
To stay compliant, businesses must:
- Follow regulations – Different countries have specific KYC laws that businesses must adhere to, such as Anti-Money Laundering (AML) rules.
- Verify customer identities – Using official documents, biometric data, and database checks to confirm authenticity.
- Monitor transactions – Continuously checking for suspicious activity to detect potential risks.
- Keep records – Storing customer verification data securely to meet regulatory requirements.
Failing to meet KYC compliance can result in heavy fines and reputational damage. By following proper procedures, businesses can protect themselves while building trust with customers and regulators.
What are the benefits of KYC?
Implementing a strong KYC process offers several key advantages for businesses and customers alike.
- Prevents fraud and financial crime – KYC helps stop identity theft, money laundering, and fraudulent activities by ensuring customers are who they claim to be.
- Ensures regulatory compliance – Following KYC guidelines helps businesses avoid fines, legal issues, and reputational damage.
- Builds customer trust – When businesses take security seriously, customers feel safer sharing their personal and financial information.
- Reduces business risks – By verifying identities and monitoring transactions, companies can identify high-risk customers early and take necessary precautions.
- Enhances security with advanced technology – Using biometric verification and AI-driven monitoring makes KYC faster, more reliable, and less intrusive for customers.
- Improves financial system integrity – KYC helps maintain a safe and transparent financial environment by preventing bad actors from exploiting financial services.
By implementing KYC effectively, businesses not only meet regulatory requirements but also create a safer and more trustworthy system for everyone involved.
KYC in the banking sector
The banking sector relies heavily on Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations to prevent fraud, money laundering, and other financial crimes. Banks must comply with strict guidelines to verify customer identities, assess risks, and ensure transparency in financial transactions.
In the U.S., the USA PATRIOT Act plays a key role in shaping KYC requirements. It mandates that financial institutions collect and verify identifying information from customers, including beneficial owners of accounts, to prevent illegal activities.
Regulatory bodies such as the Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) enforce KYC standards within the banking sector. Under FINRA Rule 2090, also known as the “Know Your Customer” rule, banks must establish customer risk profiles by gathering detailed information about their financial background and transaction history. This helps institutions assess the potential risk each customer poses.
Beyond the initial verification process, KYC in banking requires ongoing monitoring of customer accounts. Banks continuously track transactions and update customer information to detect suspicious activity and ensure compliance with evolving regulations.
By implementing these measures, the banking sector strengthens financial security, protects customers, and maintains trust in the global financial system.
How does Udentify help comply with KYC requirements?
Udentify simplifies and strengthens the KYC process by providing advanced identity verification. Through cutting-edge technology, it ensures businesses meet compliance standards while enhancing security and user experience.
With biometric authentication, AI-driven document verification, and real-time identity checks, Udentify enables organizations to quickly and accurately verify customer identities. This reduces fraud risks and ensures compliance with key regulations, including:
- USA PATRIOT Act (U.S.) – Establishes KYC and AML requirements for financial institutions.
- FINRA Rule 2090 (U.S.) – Requires firms to verify customer identities and maintain risk profiles.
- 6th Anti-Money Laundering Directive (6AMLD) (EU) – Strengthens AML enforcement and expands criminal liability.
- General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) (EU) – Ensures secure handling of customer data in compliance with privacy laws.
- Electronic Identification, Authentication, and Trust Services (eIDAS) (EU) – Regulates digital identity verification across member states.
Additionally, Udentify supports ongoing monitoring, allowing businesses to continuously assess customer risk profiles and detect suspicious activities. By automating KYC processes, Udentify helps financial institutions and other regulated entities stay compliant while improving efficiency and customer trust.









